SUPPLY CHAIN ENGINEERING
Welcome to Supply Chain Engineering, an essential discipline within Industrial Engineering.
In this page, we’ll delve into the fundamentals of Supply Chain Engineering, its significance in industrial operations, and how it contributes to optimizing processes and maximizing efficiency.
KEY AREAS OF FOCUS
Supply Chain Engineering focused on designing, optimizing, and managing the flow of goods, information, and resources from the point of origin to the point of consumption.
It encompasses a range of activities, including procurement, production planning, inventory management, logistics, and distribution.
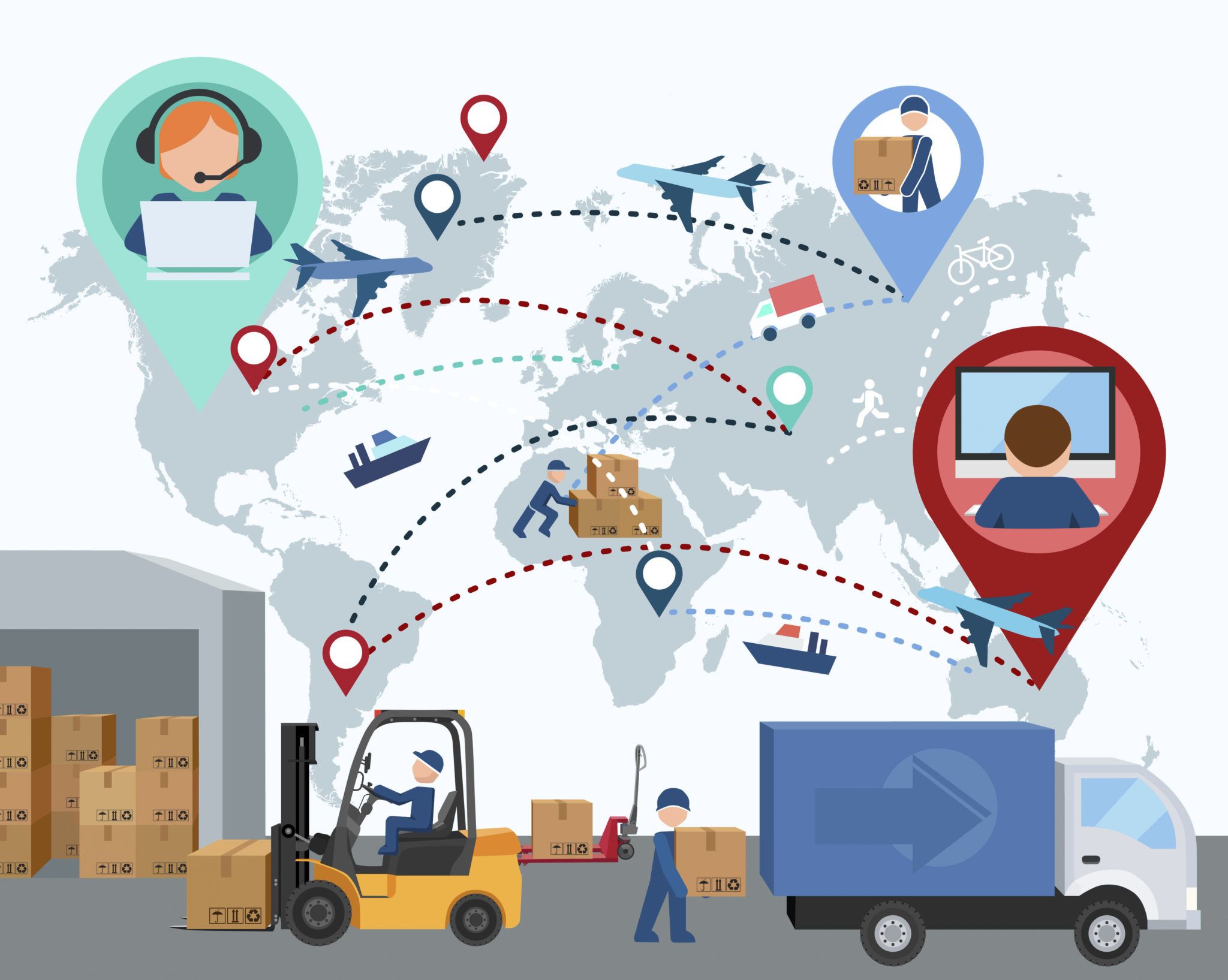
SUPPLY CHAIN ENGINEERING TASKS
Production Planning: Developing strategies to optimize production schedules, minimize lead times, and maximize resource utilization.
Procurement Management: Efficiently sourcing raw materials, components, and services from suppliers while ensuring cost-effectiveness and quality.
Warehousing and Distribution: Establishing efficient storage facilities and distribution centers to streamline the movement of goods within the supply chain.
Inventory Management: Balancing inventory levels to meet customer demand while minimizing holding costs and stockouts.
Logistics and Transportation: Designing efficient transportation networks and distribution channels to ensure timely delivery of products to customers.
PROGRAMS FOR SYSTEMS ENGINEERS
Supply Chain Planning and Optimization Tools
SAP Integrated Business Planning (IBP): A cloud-based solution for demand planning, inventory optimization, and supply chain management.
Oracle Supply Chain Planning: Provides comprehensive planning capabilities for demand management, supply planning, and production scheduling.
JDA Software (now Blue Yonder): Offers a suite of supply chain planning and optimization solutions, including demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and transportation management.
Inventory Management Systems
SAP Inventory Management: Part of the SAP ERP system, it helps organizations manage inventory levels, track stock movements, and optimize warehouse operations.
Oracle Inventory Management Cloud: Provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, enables multi-location management, and supports inventory optimization.
WMS (Warehouse Management Systems): Software systems that optimize warehouse operations, including receiving, picking, packing, and shipping.
Transportation Management Systems (TMS)
MercuryGate TMS: Offers transportation planning, execution, and optimization capabilities for shippers, carriers, and logistics service providers.
Oracle Transportation Management (OTM): Provides transportation planning, execution, and freight payment capabilities to streamline logistics operations.
Manhattan Associates TMS: Offers transportation planning, execution, and visibility solutions to optimize transportation networks and reduce costs.
Supply Chain Analytics and Business Intelligence Tools
Tableau: Data visualization software that helps organizations analyze and visualize supply chain data to gain insights and make data-driven decisions.
Power BI: Business intelligence platform that enables organizations to create interactive reports and dashboards to monitor supply chain performance and KPIs.
Qlik Sense: Data analytics and visualization software that provides self-service analytics capabilities for exploring and analyzing supply chain data.
BENEFITS OF SUPPLY CHAIN ENGINEERING
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Meeting customer demand promptly and reliably improves customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Risk Mitigation: Supply Chain Engineering helps identify and mitigate risks, such as supply chain disruptions and inventory shortages.
Sustainable Practices: By optimizing resource utilization and reducing environmental impact, Supply Chain Engineering promotes sustainability.
Improved Efficiency: Streamlining processes and systems for better performance.