SYSTEMS ENGINEERING
Welcome to Systems Engineering, a pivotal branch of Industrial Engineering. In this article, we’ll explore what Systems Engineering entails, its core principles, the processes involved, and how it applies across various industries to enhance complex systems.
Whether you’re a student, professional, or enthusiast, this guide will provide valuable insights into this critical field.
KEY AREAS OF FOCUS
Systems Engineering is an interdisciplinary field that focuses on designing, integrating, and engineer systems throughout their life cycles.
It ensures that all aspects of a system are considered and integrated into a cohesive and efficient whole, addressing both technical and human-centered requirements.
SYSTEMS ENGINEERING EXPLAINED
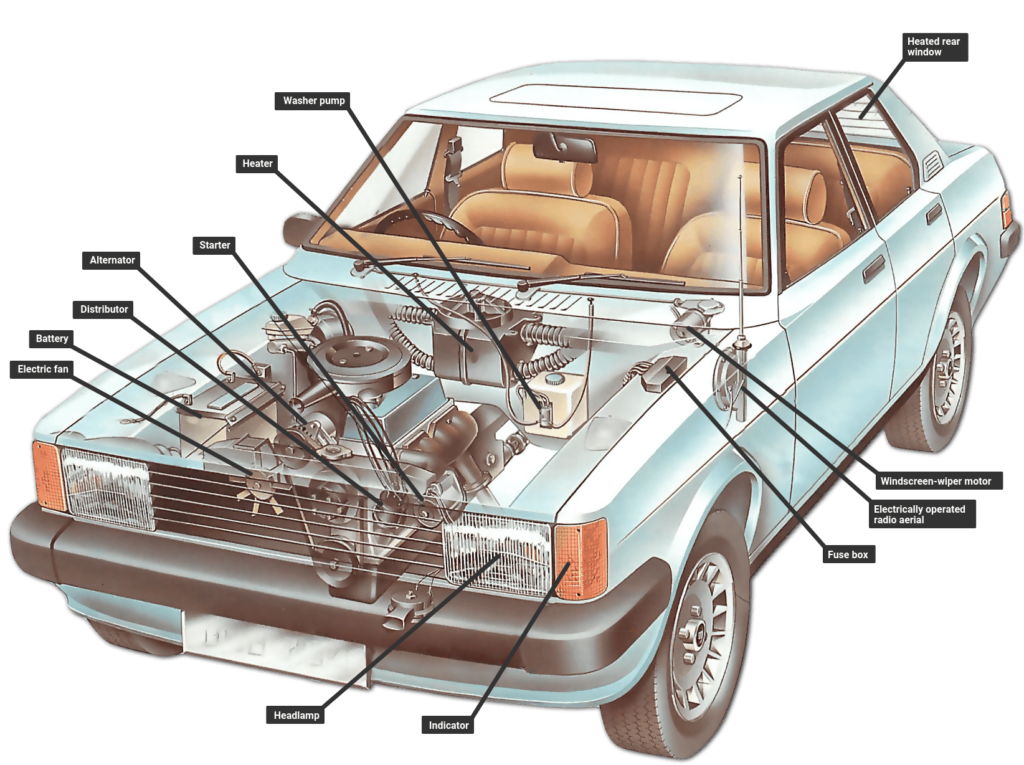
Let’s use building a car as an example.
Mechanical engineers focus on the engine and other mechanical components; electrical engineers handle the wiring and electrical systems; computer engineers develop the software that controls various functions of the car.
However, none of these individual systems alone makes up a complete car. This is where systems engineers come in. They work to integrate each individual system into a cohesive whole, creating a functional and efficient car from these disparate parts.
In essence, systems engineers serve as the bridge between different engineering disciplines, ensuring that all components work together seamlessly. They play a crucial role in the success of projects by coordinating and integrating various systems into a unified, operational product.
PROGRAMS FOR SYSTEMS ENGINEERS
Modeling and Simulation Tools
MATLAB/Simulink: Widely used for multi-domain simulation and model-based design.
SysML (Systems Modeling Language): A modeling language used to specify, analyze, design, and verify complex systems.
ModelCenter: A software suite for modeling and simulation integration.
Configuration Management Tools
IBM Engineering Workflow Management (EWM): Integrates with other IBM tools for end-to-end lifecycle management
PTC Windchill: Product lifecycle management software that helps with configuration management.
Subversion (SVN): An open-source version control system.
Risk Management Tools
Reliability Workbench: A comprehensive tool for risk and reliability analysis.
RiskWatch: A risk assessment and management software.
Isograph: Provides reliability, availability, and risk assessment tools.
BENEFITS OF SYSTEMS ENGINEERING
Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks throughout the system lifecycle.
Cost Savings: engineer systems to reduce costs and optimize resources to prevent costly rework.
Enhanced Quality: Ensuring high standards of quality and reliability in system design and implementation.
Improved Efficiency: Streamlining processes and systems for better performance.