DATA ANALYSIS INTRODUCTION
Step into the realm of data-driven decision-making with our industrial engineers’ expertise in data analysis.
Through cutting-edge analytics, we uncover actionable insights that drive strategic decision-making and operational excellence. We delve into how to leverage data and optimize processes, boost efficiency, and drive innovation across industries. Explore how our analytical prowess can transform your business landscape.
What is the purpose of Data Analysis in Industrial Engineering?
BUILDING BLOCKS OF SIX SIGMA AND LEAN
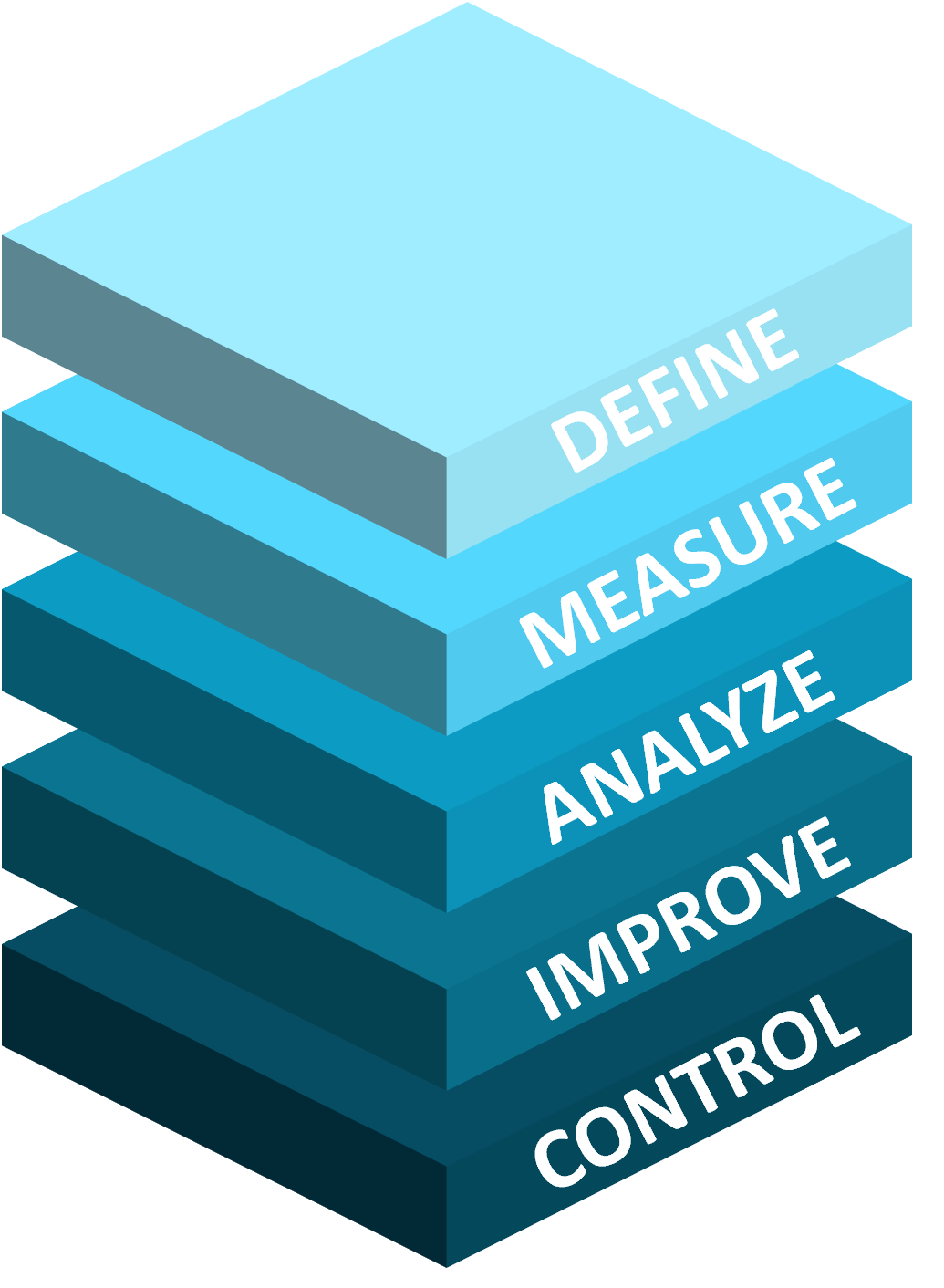
WHAT IS SIX SIGMA?
A powerful methodology for improving processes and reducing defects. Rooted in data-driven decision-making, Six Sigma aims to minimize variation and optimize performance to achieve near-perfect outcomes. Join us as we explore the principles and techniques of Six Sigma to drive excellence and efficiency in your organization.
HOW TO PERFORM DATA ANALYSIS?
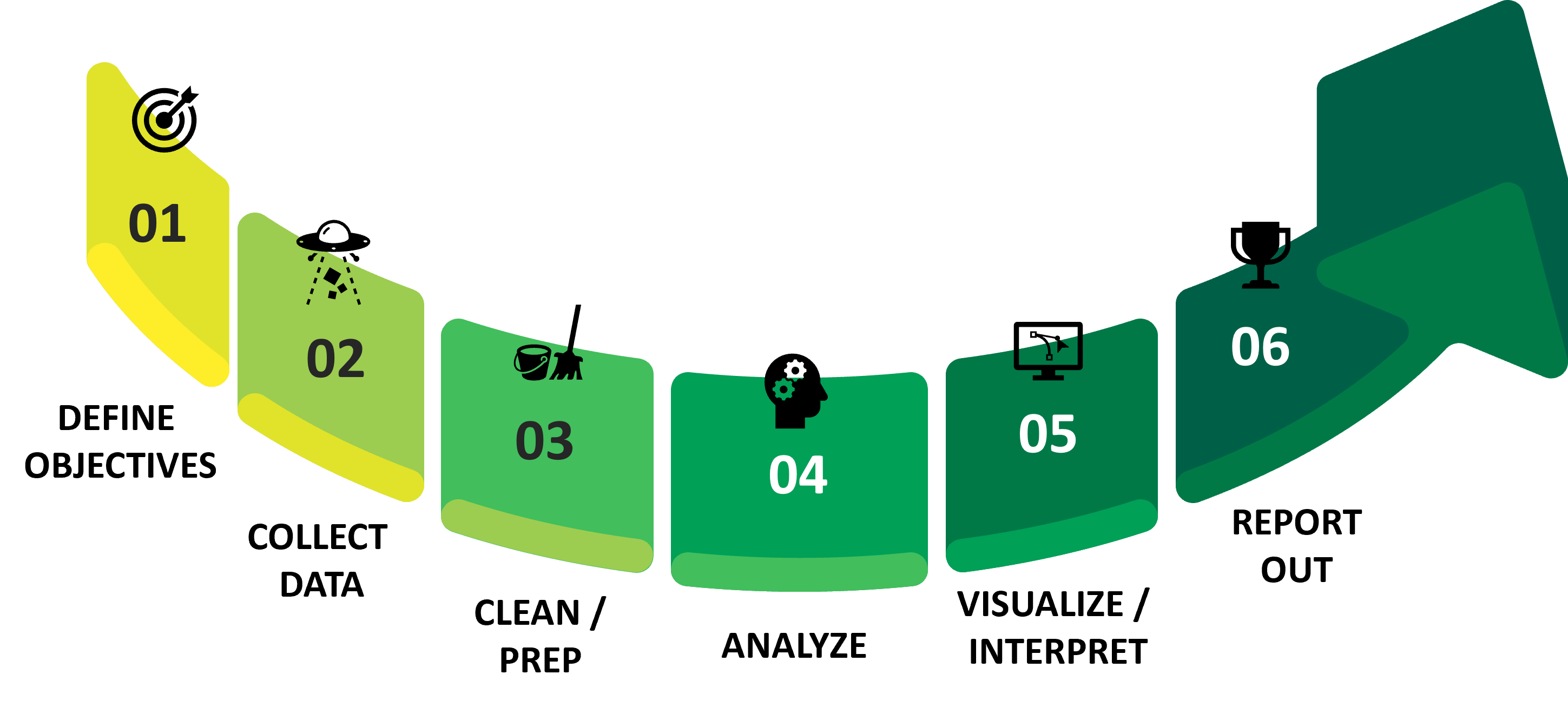

What are the Methods / Programs?
Microsoft Excel is a tool for organizing, manipulating, visualizing, and analyzing data via spreadsheets, with functions, formulas, and charting options.
MySQL is a database management system for storing, querying large datasets, supporting complex data analysis through SQL (Structured Query Language).
Microsoft Access is a user-friendly database system, able to streamline storage, retrieval, and analysis through customizable forms, queries, and reports.
Tableau is a data visualization tool for creating interactive, shareable dashboards that turn raw data into insights.
Minitab is a statistical software that simplifies analysis, quality improvement, and visualization through user-friendly tools.
PRO vs CON
Overview of Data Programs