WHAT IS HYPOTHESIS TESTING?
Hypothesis Testing is a statistical method used to make inferences or draw conclusions about a population based on sample data. It involves testing an assumption (hypothesis) about a population parameter to determine whether the evidence in the sample data supports or refutes that assumption.
KEY TESTING CONCEPTS
Null Hypothesis (H0): The default assumption or claim that there is no effect or no difference. It is what we seek to test against.
Alternative Hypothesis (HA): The opposite of the null hypothesis. It represents the claim that there is an effect or a difference.
Significance Level (α): The probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true. Common significance levels are 0.05, 0.01, and 0.10.
Test Statistics: A standardized value calculated from sample data, used to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis. Examples include the Z-score, t-score, and chi-square statistic.
P-value: The probability of observing the test statistic or something more extreme, given that the null hypothesis is true. A low p-value (typically ≤ 0.05) indicates strong evidence against the null hypothesis.
Steps in Conducting Hypothesis Testing
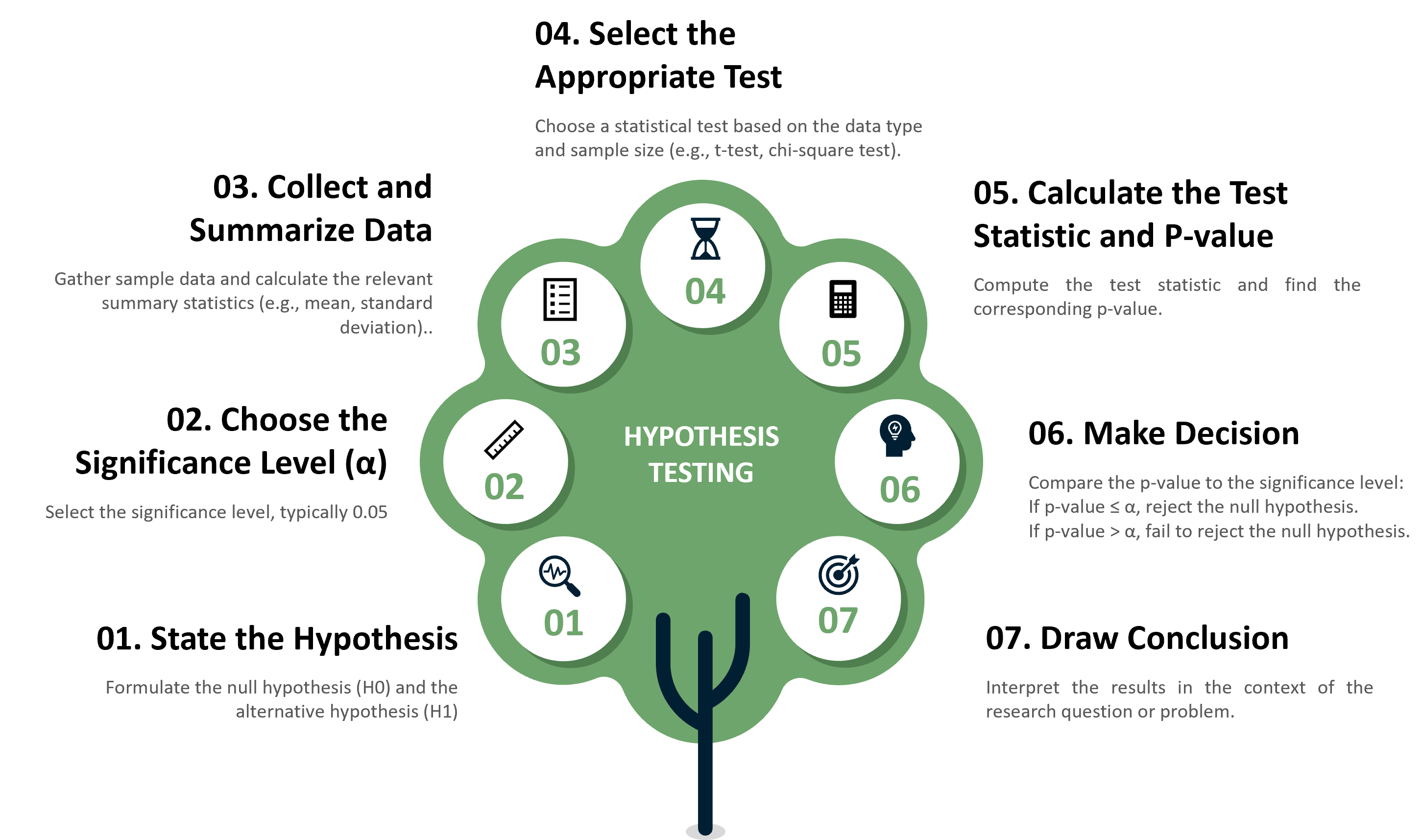
TYPES OF HYPOTHESIS TESTS
One-Sample t-Test
Tests whether the mean of a single sample differs from a known population mean.
Two-Sample t-Test
Compares the means of two independent samples to see if they differ significantly.
Paired t-Test
Compares means from the same group at different times or under different conditions.
Chi-Square Test
Tests the association between categorical variables or the goodness-of-fit for categorical data.
ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)
ANOVA compares means among three or more groups to see if at least one group mean is different.
Regression Analysis
Regression tests the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables.
PRO vs CON

MPORTANCE OF TESTING
Decision Making: Provides a systematic way to make data-driven decisions.
Scientific Research: Essential for validating research findings and theories.
Quality Control: Helps in assessing and improving process performance.
Business and Economics: Used to evaluate market strategies, financial models, and economic hypotheses.
APPLICATIONS OF TESTING
Healthcare: To test the effectiveness of new treatments or drugs.
Manufacturing: To compare the quality of products from different production lines.
Marketing: To assess the impact of different marketing strategies on sales.
Education: To evaluate the effectiveness of teaching methods or curricula.