WHAT IS PROCESS CAPABILITY ANALYSIS?
Process Capability Analysis is a statistical method used to determine the ability of a manufacturing process to produce products within specified limits. It evaluates the inherent variability of a process and compares it to the specification limits to see how well the process can meet the requirements.
KEY PROCESS CAPABILITY CONCEPTS
Specification Limits (Specs)
These parameters encapsulate the acceptable range of values for a product or process, often outlined by customer specifications and requirements.
Upper Specification Limit (USL): The maximum acceptable value.
Lower Specification Limit (LSL): The minimum acceptable value.
Control Limits
These represent statistical boundaries that a process must adhere to in order to maintain control. Determined from process data, they are usually established at ±3 standard deviations from the process mean.
Process Capability Indices
Cp (Capability Index): Measures the potential capability of a process by comparing the spread of the process variability to the spread of the specification limits. It is calculated as:
Cp=USL−LSL6σ
σ is the standard deviation of the process.
Cpk (Capability Index for Centering): Measures the actual capability of the process, taking into account the mean shift. It is calculated as: Cpk=min(USL−μ3σ,μ−LSL3σ)
μ is the process mean.
Pp and Ppk (Performance Indices): Similar to Cp and Cpk, but these use overall (long-term) process data rather than short-term data.
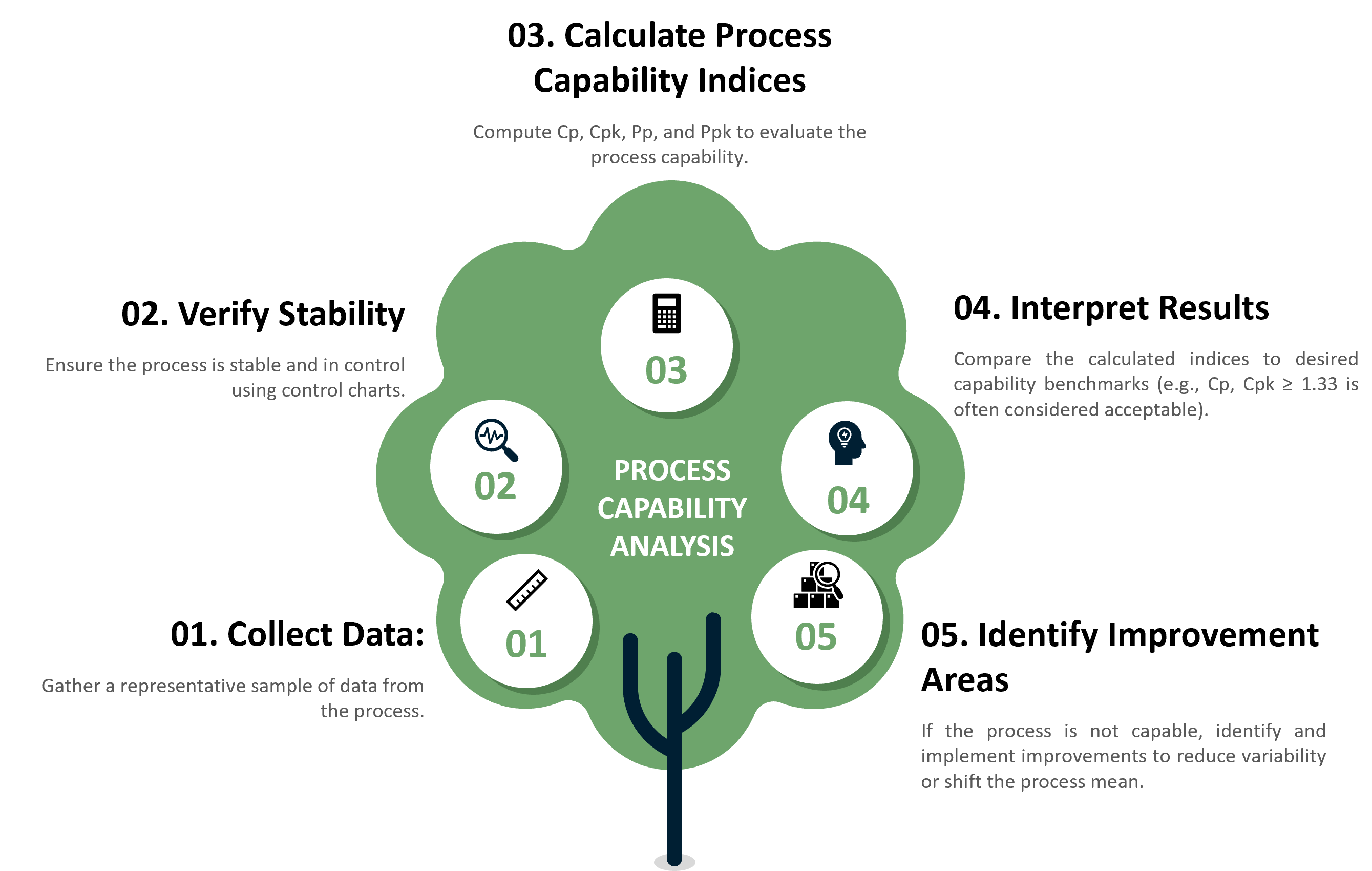
Steps in Conducting Process Capability Analysis
MPORTANCE OF CAPABILITY ANALYSIS
Tolerance Testing: Ensures that the process operates optimally within existing tolerances, it possesses the capability to offer quantitative insights into the performance and stability of manufacturing processes.
Quality Assurance: Ensures that the process can consistently produce products that meet specifications.
Process Improvement: Identifies areas where the process can be improved to reduce variability and improve performance.
Customer Satisfaction: Helps in meeting customer requirements and expectations by maintaining high-quality standards.
APPLICATIONS OF TESTING
Manufacturing: To ensure that production processes can produce parts within specification limits.
Healthcare: To assess and improve the capability of clinical processes.
Service Industry: To evaluate and enhance the performance of various service processes.
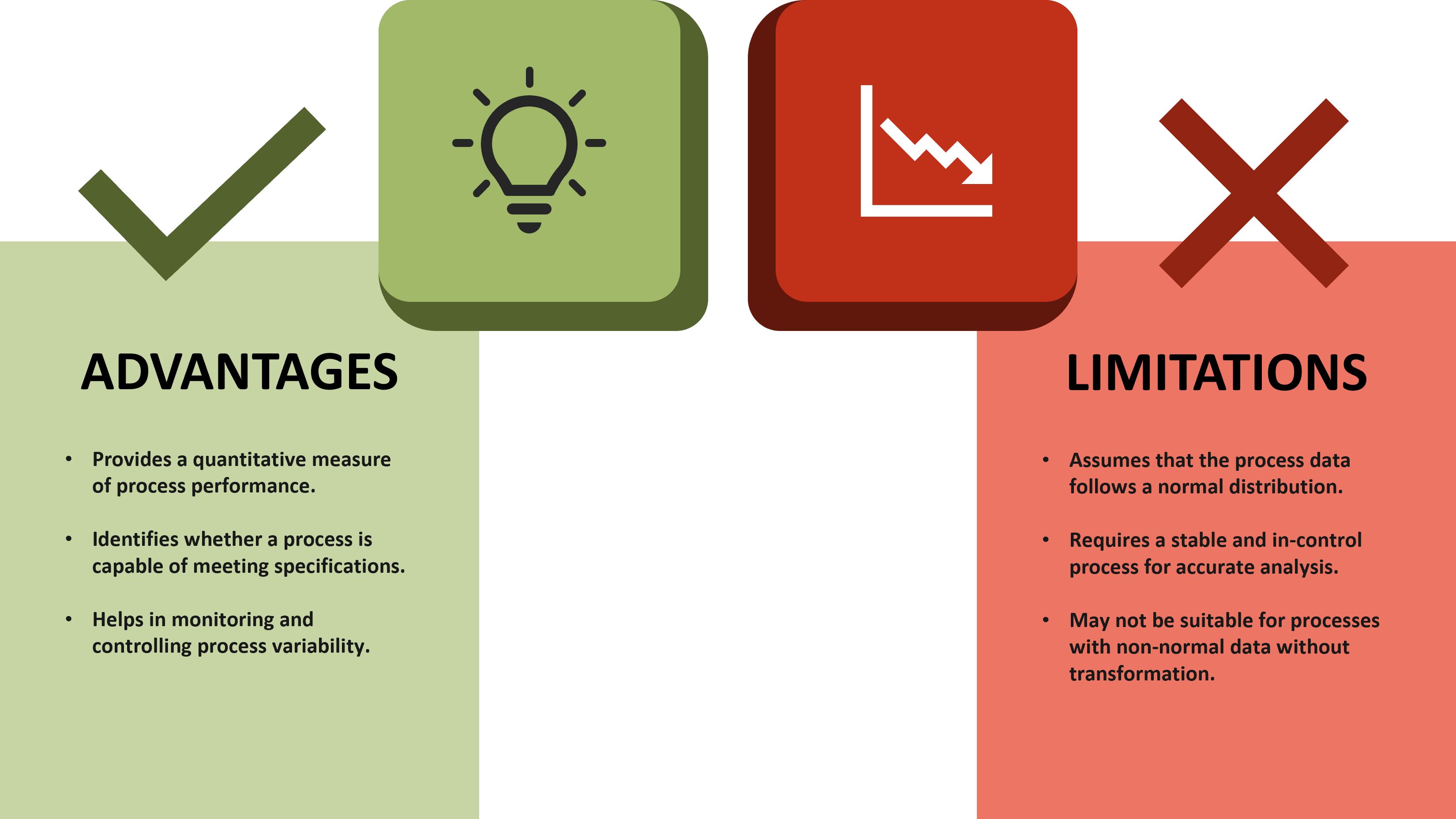
PRO vs CON