WORK SAMPLING INTRODUCTION
Welcome to our exploration of Work Sampling Time Studies, a method of Direct Observation Time Standards.
The Work Sampling Time Standard Method is a Direct Observation technique used to assess productivity and efficiency in a variety of industries. It involves randomly observing and recording activities performed by workers over a specified period. By collecting data on tasks, frequencies, and durations, organizations can gain insights into workflow patterns and identify areas for improvement.
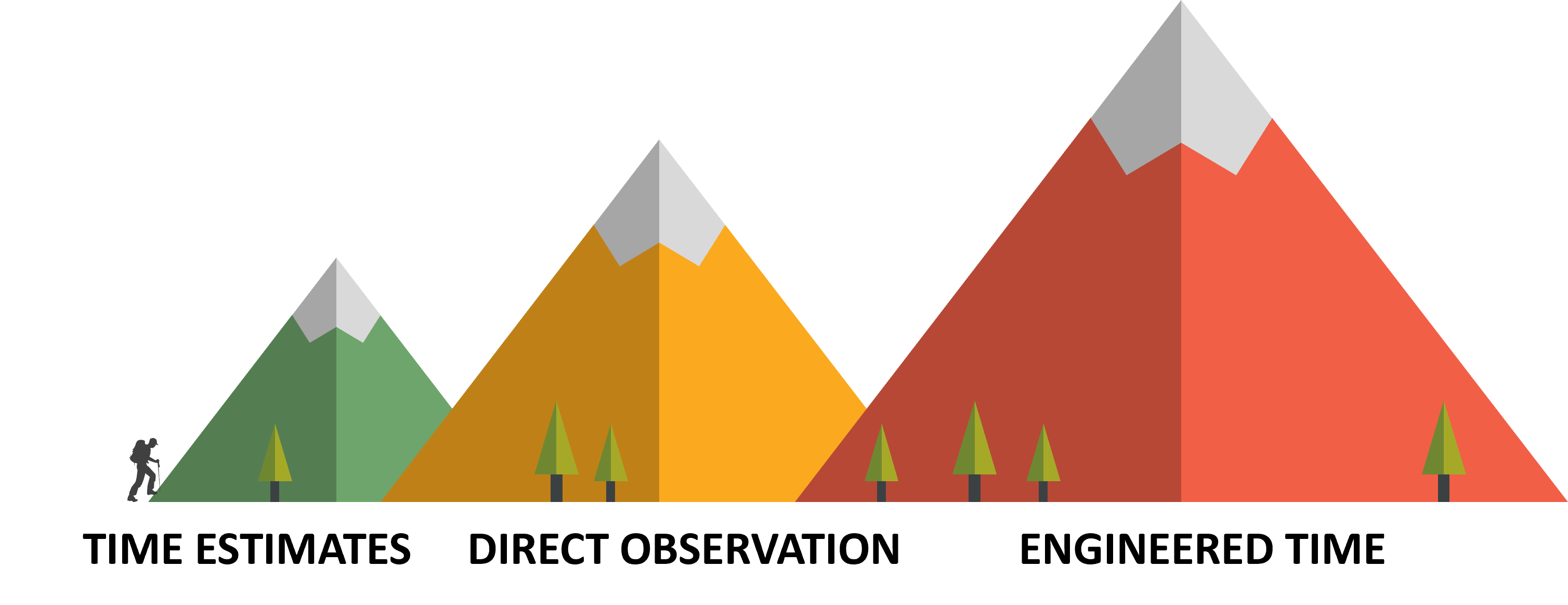
When do we use Work Sampling as a method for our Time Standard?
Similar Work Content, useful for repetitive and similar work across a build as the process steps tend to blend together.
Detail is Not Crucial, random work observations will lead to missed details, advised to use during a repetitive process.
HOW TO PERFORM A WORK SAMPLING STUDY?
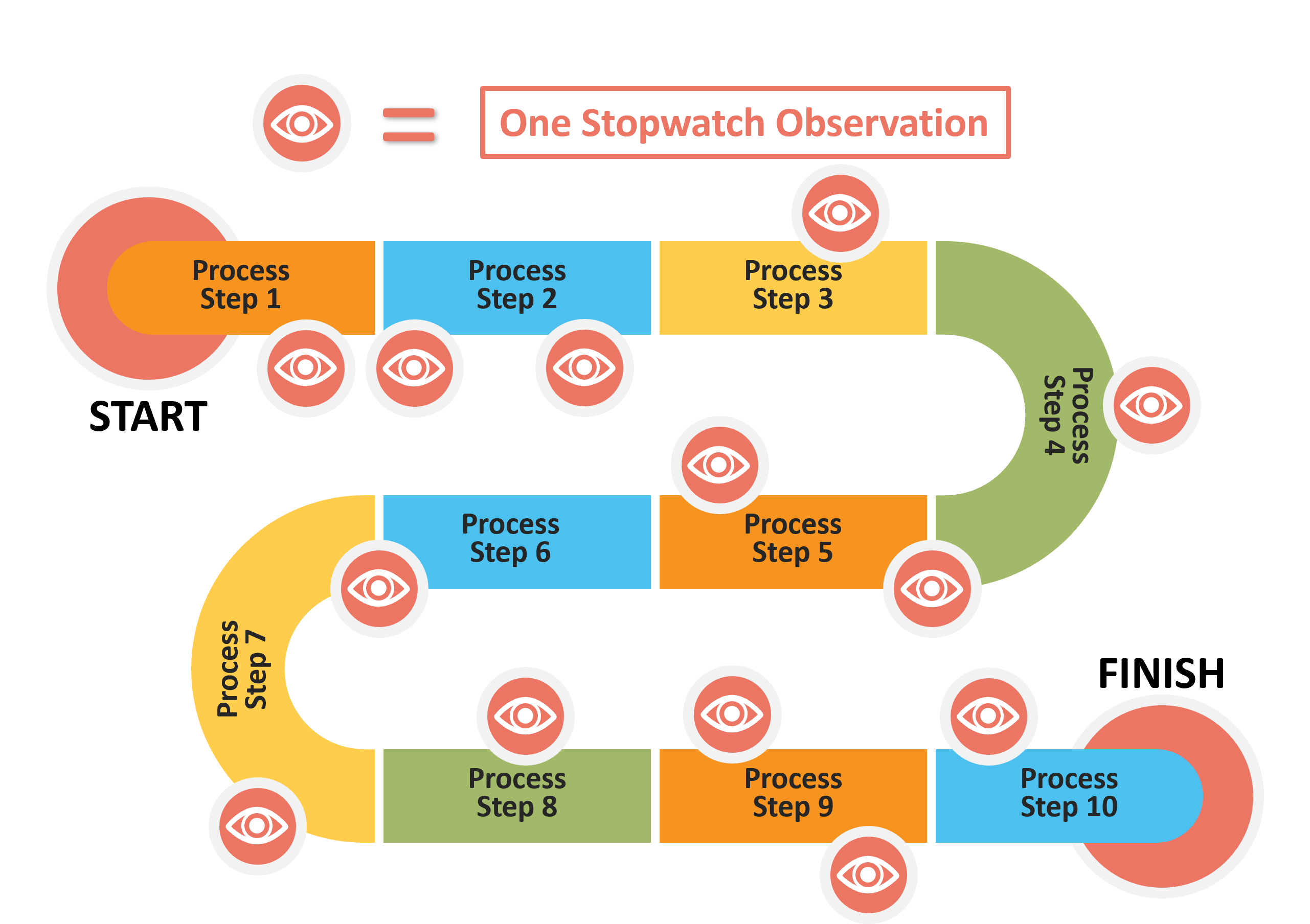
Observations are conducted randomly throughout the Sampling Study and the Start to Finish times are used to calculate Total Process Time.
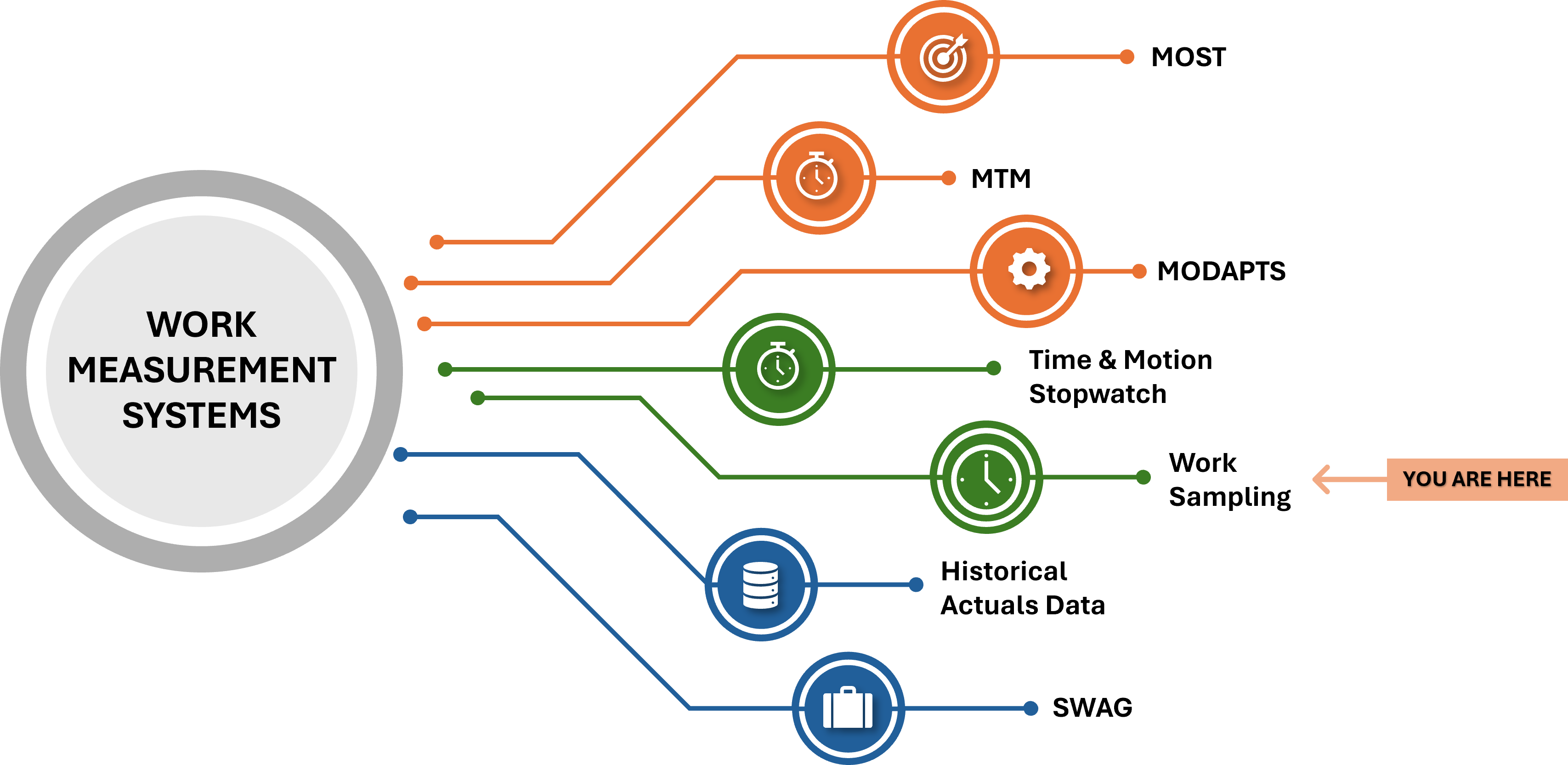
LEARN ABOUT THE OTHER TIME STANDARD METHODS BELOW:
PRO vs CON
Overview of Benefits and Cons of Time Standard Type